While often confused, bookkeeping and accounting serve separate and distinct functions in the running of a business. Bookkeeping is the function of documenting and maintaining records of transactions. Accounting, on the other hand, is the act of actually analyzing and interpreting the documentation and turning into meaningful data. While bookkeepers maintain the data needed to file your taxes, an accountant is likely the one who will actually prepare and file your taxes. Learn more about bookkeeping and accounting.
Personalized expert assistance
We provide you with a dedicated bookkeeper backed by a team of experienced small business experts. Connect directly with your team through desktop or mobile, ensuring professional support is just a few swipes, taps, or clicks away.
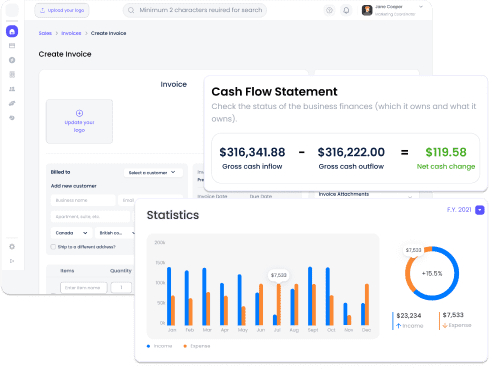
Robust financial reporting
Our platform delivers monthly financial statements and expense summaries to empower you with control over your finances. Visual reports at a glance provide a comprehensive view and actionable insights, ensuring you're always well-informed and equipped to drive your business forward. Say goodbye to uncertainty.
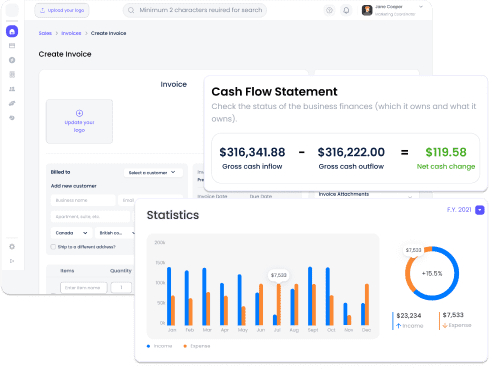
Instant insights right at your fingertips.
Access your up-to-date financial data whenever you log in. Real-time insights enable you to make quick decisions on spending and saving, ensuring your business stays on budget.
Tax season, without the anxiety.
Our standard offering includes a year-end package that contains all the necessary components for your filing needs. If you choose to upgrade your plan, you can further streamline your tasks. With our Premium plan, you gain access to expert tax preparation, filing assistance, and year-round tax advisory support.
Frequently Asked Questions
A bookkeeper is a person employed to keep the records and financial affairs of a business. Bookkeepers are responsible for some (or all) of an organization’s financial information, which is generally known as the General Ledger. These Ledgers include balance sheets and income statements. They also record financial transactions in the form of debits or credits in the ledger, as well as create financial reports.
Payroll processing is the administrative process around maintaining employee records, including salaries, bonuses, wages, tax withholding, and deductions. It also refers to the actual act of paying employees. The process of maintaining payroll records is complicated and deeply important for maintaining IRS compliance.
If you’re a freelancer or contractor, or you own and operate a small business, the IRS requires that you pay Estimated Taxes four times a year. Estimated taxes apply to any taxable income that you receive without any tax being withheld, including:
- Interest
- Stock dividends
- Capital gains
- Income earned through self-employment
The quarterly estimated tax deadlines each year fall on:
- Q1 – April 15th
- Q2 – June 15th
- Q3 – September 15th
- Q4 – January 15th of the following year.
*Note: If the due date for making an estimated tax payment happens to fall on a Saturday, Sunday, or legal holiday, the payment will still be on time if you make it on the next non-weekend or legal holiday day.

